Add, copy, paste, move, delete an element in the object tree.
Objects are organized into a tree for convenient grouping and manipulating multiple objects as a single whole. The object tree always has a root element, which is called scene and contains all other objects. A scene consists of objects, an object has a type and consists of properties, and properties have values. Object values are configured in the right column.
Adding. In the toolbar located at the top of the screen, click the "Plus" and choose the type of object you want to add. The added object has the following default values: Position 0-0-0; Rotation: 0-0-0; Scale: 1-1-1.
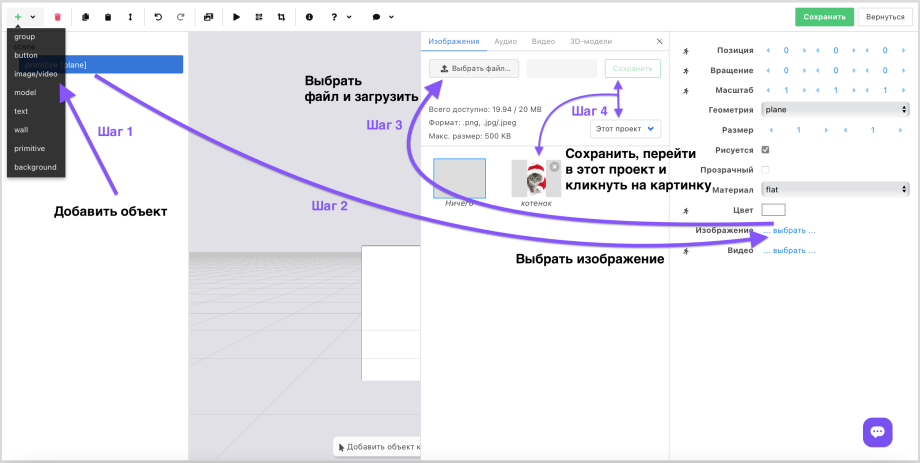
To add an image, video, or 3D model, you need to add the corresponding object, upload a file from your computer or select one from those available in the builder and click on it.
At the moment the aspect ratio of an uploaded image or video is not preserved. You need to change the scale manually. We will improve this soon.
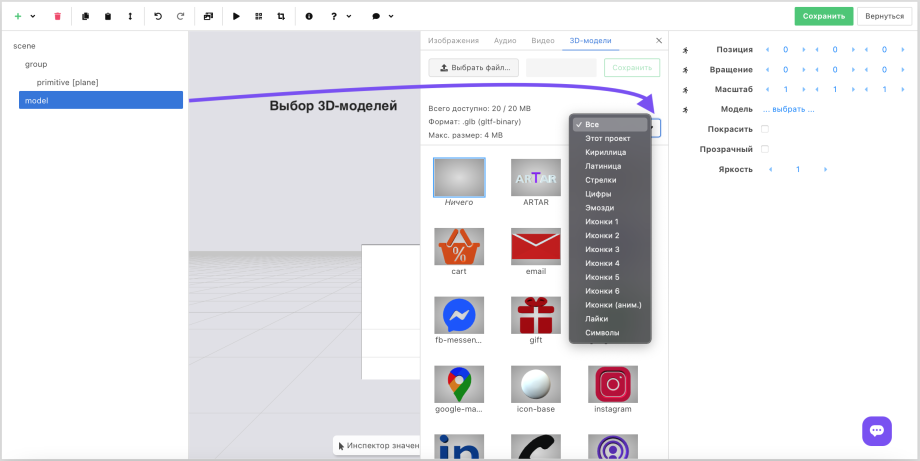
Note that the added object will be nested under the selected element and will belong to the "parent", i.e., the values we set (or have already set) for the "parent" will directly affect the child element. This means that by changing the size or, for example, moving the parent object we move all child objects nested within it.

Deletion. To delete an object, select it and click the "Trash" in the control panel. When deleting a parent object, all child objects nested within it are deleted.
Copying. Select the object you want to copy, click the "Copy" icon in the control panel, select "Scena" or the element in which you want to nest the copied object and click "Paste". If the copied object contains sub-objects, they are copied as well.
Moving. Select the object you want to move, move the cursor to the desired location and click to paste.
This instruction is relevant if you need to move an object within the tree structure. In this case, the object may not change its position in the editor's visual window and in AR. How to move, that is change position, in coordinate space (in the AR layer) is discussed below.